Overview
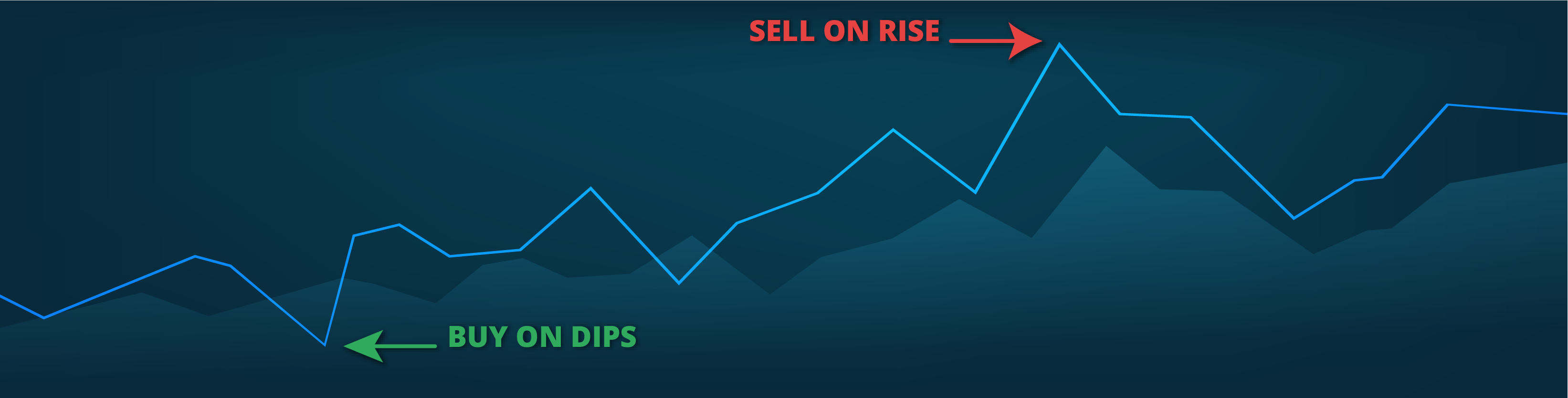
Imagine buying something on sale and then selling it later for a profit. Although it’s a little more complex, in essence, this is how the “buy, the dip” trading strategy works. You buy a financial assetA stock, commodity, currency, index or any other entity one may trade or invest in. when its price suddenly drops with the expectation that you can sell it for profit once its price recovers or starts rising.
Investing legend Warren Buffett, chairman and CEO of Berkshire Hathaway Inc and a famous business magnate and philanthropist, is a significant proponent of this strategy for American stocks. According to him, it is next to impossible to go wrong when you invest in the U.S. economy because the stock marketA location or entity where people and entities can negotiate and trade assets of value. always recovers.
While this strategy is commonly associated with stocks, “buying the dip” can be used in all types of assets, including indices, currencies, commodities, and even cryptocurrencies.
The rationale behind buying the dip is that it’s common during a downtrendA chart pattern showing diminishing value and confirmed by sequentially falling highs and lows., and higher prices usually follow these. However, there is the riskThe level of deviation of past returns and/or losses on an asset from the mean. Usually, the higher ... that when an uptrend ends, prices could dramatically go lower and take a long time to recover.
With this in mind, it is imperative to be aware of the pros and cons of the “buy, the dip” strategy before applying it to your trading plan.
The Advantages of Buying the Dip
When you buy the dip, you purchase a good asset when its price drops because you believe it will rebound and bring future profits. You are essentially buying low in the hopes of selling high, which is one of the fundamental investing strategies.
Thus, buying the dip is most useful when you are the buy-and-hold type or a long-term investor and exemplified in the following approaches:
- Value Investing – in this approach, you buy stocks that you believe are underpriced or are trading below their company’s intrinsic worth. While you can buy the stock at any time, you prefer to wait for its price to dip so you can purchase them at a better bargain.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging – in this approach, you buy shares at set intervals to average out the volatilityThe measure of fluctuation in an asset’s value from the mean. Volatility can be historical (over a... and cost of the stock. If the stock is on a downtrend, you will be buying the dip at the said intervals. Continuously buying the dip is called averaging down, and this happens when you keep on buying stocks that are on the downtrend to realize profits sooner.
By buying the dip, an investor can reap financial benefits because it increases the chance of profits sooner. However, this is not a fail-proof strategy, considering other factors such as your time horizon as some assets may take a long time to recover.
The Disadvantages of Buying the Dip
Like all trading strategies, investors must also be wary of the risks when buying the dip as it does not guarantee profits.
One of the most significant risks in buying the dip is that the asset price will not increase again or take a very long time to recover. When this happens, a traderA merchant who purchases and sells assets or services for profit. In financial markets, the trader b... may get stuck in his positionAn open trade or transaction. A position can be long (a contract to buy the asset) or short (a contr... or take a significant loss when he decides to exit the market, especially if he has been averaging down.
Another risk when buying the dip is that there is no surefire way to distinguish if the decreasing price of the asset is a temporary drop or a sign that prices are about to go much lower. Dips is where an investor’s knowledge of the market and other investing strategies can come in handy. It can help make educated decisions on whether the cause of the dip is superficial or goes to the fundamental aspects of the company behind it.
Key Takeaway
The importance of risk control cannot be underestimated when it comes to your investmentAn asset (usually money or work) provided to another in expectation of receiving a cash return or be... and trading plans—as with all other strategies and methodologies, buying the dip is not ideal in all scenarios and has many factors affecting its effectiveness.
Buying the dip usually works better with assets in uptrends, where prices are making higher lows and higher highs. The logic is that an increase usually follows a dip in the asset’s price.
When the price of an asset enters a downtrend, investors should be wary of buying the dip as the price will get cheaper and cheaper, with each dip followed by lower prices.
Overall, it is essential to remember that buying the dip is just one of the countless strategies available to an investor. There is no one-size-fits-all formula for trading, but with research and learning from other seasoned traders, investors can develop a plan that works best with their needs.
To learn more about trading and investing, sign up for a FREE account now at Queensway Academy.